Over-The-Air (OTA) is a common concept that enables you to distribute various things, like a piece of code, to a device without physical access. In the context of mobile networks and SIM cards, OTA technology enables mobile network operators (MNOs) or MVNOs to change or update data in SIM cards deployed and get service without reissuing them! So, it means through remote provisioning, OTA reduces the cost of manual configuration not only for carriers but also for subscribers.
In the fast-growing eSIM and IoT field, which the content of the SIM or eUICC on a consumer or M2M device needs to be changed according to the subscriber or network demands, the OTA, also known as OTA provisioning, is a mandatory requirement. Operators must communicate with SIM, introduce new services, upload or update their profiles or update firmware rapidly and cost-effectively. So all of these actions are possible through OTA. OTA also is very important from a security perspective; it helps to keep devices updated and apply security patches, bug fixes, or the latest optimized configurations quickly. Although over-the-air provisioning will be established through a secure channel.
Let’s take a look at how we can implement the OTA now that we know what it is and why it’s needed.
What is the OTA Gateway?
The OTA gateway or sometimes referred to OTA platform is an element in the operator network or service providers which enables the firm to use OTA technology and manage SIMs or eUICCs. OTA gateways usually receive SIM management requests through an API like RESTful API and then create an appropriate data format that SIM cards can understand. In the next step, the OTA gateway sends the formatted service request as a message (SMS) to the SMSC. SMSC delivers the SMS through the cellular network to the recipient’s SIM card. OTA usually uses SMS to communicate with SIM, but there are other methods like HTTP(s) which let the SIM card retrieve data from the operator or central servers that are specified.
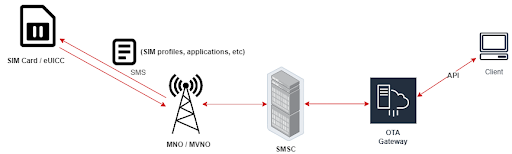
In the IoT field, it is usual that the service provider does not have the whole operators’ core infrastructure, and provisioning remote devices is impossible. So in this case, some other companies or operators provide OTA gateway as a service.
The OTA gateway services provide RESTful APIs to receive requests from IoT providers or MVNOs, then transform to send them to SMSCs via SMPP.
SMSC owner can be the carrier, or it might be another service from the OTA service provider. This solution will be cost-effective with zero CAPEX and allows SPs to deploy value-added SIM applications and new services for eSIM M2M and IoT.